Why can’t Yujian Popular Science see the sun after taking some medicines?
I heard that sun exposure can cause adverse drug reactions? Some drugs can’t see the sun after taking them, so they need to "avoid the light"? Summer is coming. In order to prevent people from being inadvertently poisoned by "photosensitivity", today I will tell you what this is all about.
What is the photosensitive reaction?
Some drugs, after being taken, can cause allergic reaction of human body under the stimulation of light, which is called photosensitive reaction. Its symptoms are similar to solar dermatitis or sunburn rash, such as erythema and edema, accompanied by itching and burning pain; Or pigmentation occurs, and in severe cases there are blisters or erosive ulcers.
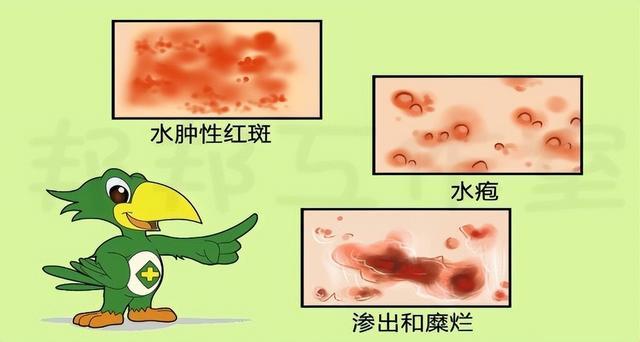
Photosensitive reactions include phototoxic reactions and phototoxic reactions. Phototoxic reaction has nothing to do with the autoimmune system, and can occur in anyone without incubation period. Generally, it can occur within a few minutes to a few hours after the first drug is irradiated by sunlight, mostly at the exposed site. After stopping the drug or avoiding light, the reaction can quickly subside. Photoallergic reaction is a kind of delayed allergic reaction related to the autoimmune system, which can be triggered by a small dose of light or weak sunlight. It usually occurs in a small number of allergic people, with a incubation period of 24 ~ 48 hours, and symptoms can occur all over the body, not just in the exposed parts. This kind of reaction lasts for a long time and can develop into a chronic and persistent photosensitive reaction.
What drugs can cause photosensitive reactions?
There are many drugs that can cause photosensitive reaction. Here are some common drugs.
Quinolone antibiotics: including sparfloxacin, lomefloxacin, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin, etc. It is clearly pointed out in the instructions of levofloxacin capsules that after exposure to sunlight or ultraviolet rays, moderate to severe photosensitive/phototoxic reactions will occur, which can be manifested as excessive sunburn reaction, so excessive exposure to light sources should be avoided. In order to reduce the adverse reactions of such drugs, it is generally recommended to take drugs every night.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: including aspirin, ibuprofen, diclofenac sodium, meloxicam, piroxicam, sulfasalazine, etc. Such drugs can cause photosensitive/phototoxic reactions, and once they occur, they should be stopped immediately.

Cardiovascular drugs: Nifedipine, Nimodipine, Amiodarone, Captopril, Benazepril, Enalapril, Indapamide, Valsartan, Losartan, etc. can cause photosensitive reaction. These drugs are generally chronic diseases and need to be taken for a long time. Therefore, patients need to strengthen safety awareness and avoid excessive sun exposure or exposure to light sources during medication.
Sulfonylurea hypoglycemic drugs: including glibenclamide, glimepiride, glipizide, etc. Such drugs can cause photo-allergic reactions. Diabetic patients should also pay attention to the adverse reactions of such drugs if they take them for a long time.
Other drugs: including tetracycline drugs (minocycline, doxycycline, etc.), sulfonamides, anti-tuberculosis drugs (pyrazinamide), digestive system drugs (ranitidine, omeprazole, pantoprazole, etc.), antidepressants (fluoxetine), retinoic acid (isotretinoin), etc.
How to prevent photosensitive reaction?
If you use the above drugs, you should pay attention to sun protection during the medication and at least 5 days after stopping the drug; Try to avoid traveling during periods of strong sunshine. In the event of a rash or skin reaction, you can immediately stop taking medicine or sunscreen, and at the same time, cold compress the red, swollen and hot parts. If the symptoms are still not relieved, go to the dermatology department in time.
Authors: The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Liu Chong, Chen Chengqun and Shi Xiangfen.