Preliminary accounting results of GDP in the third quarter of 2024
According to relevant basic data and gross domestic product (GDP) accounting methods, after preliminary accounting, China’s GDP accounting results in the third quarter of 2024 are as follows.
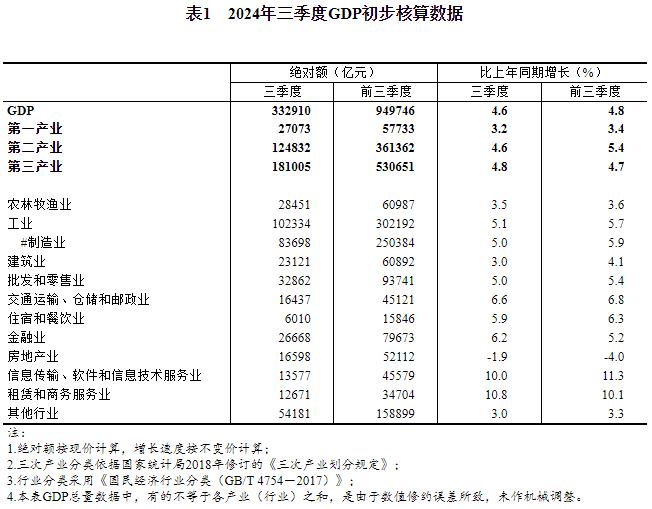
Click Download: Related Data Sheet
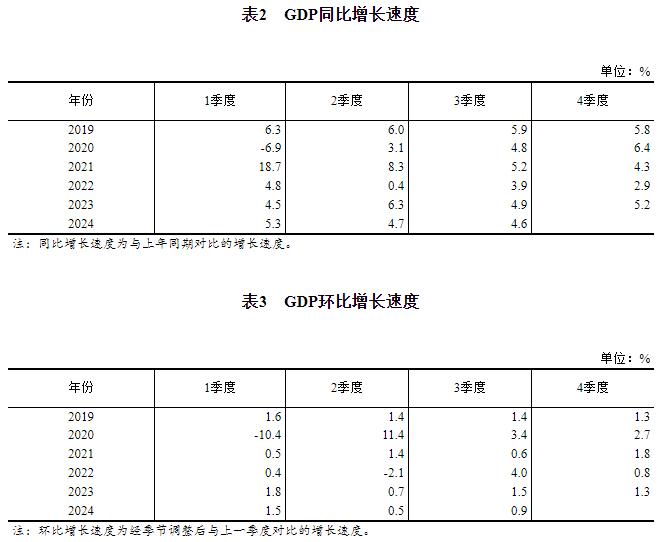
Other relevant accounting results can be found in the database of the National Bureau of Statistics.
Attachment:
China GDP Quarterly Accounting Description
1. Overview of quarterly GDP accounting
1.1 Basic concepts
GDP is the final result of the production activities of all permanent units in a country in a certain period of time. GDP is the core index of national economic accounting, and it is also an important index to measure a country’s economic situation and development level.
There are three methods of GDP accounting, namely, production method, income method and expenditure method, which reflect the results of national economic production activities from different angles. Production method is a method to get added value by excluding intermediate goods and services from the value of goods and services created in the production process. The formula for calculating the added value of production method in various industries of national economy is as follows: added value = total output-intermediate input. Add up the added value of production method in various industries of the national economy to get the GDP of production method. The income method is to account for the results of production activities from the perspective of income generated by the production process. According to this calculation method, the added value consists of four parts: workers’ remuneration, net production tax, depreciation of fixed assets and operating surplus. The calculation formula is: added value = remuneration of workers+net production tax+depreciation of fixed assets+operating surplus. The sum of the added value of income method in all industries of the national economy is equal to the gross domestic product of income method. Expenditure method is a method to calculate the gross domestic product from the perspective of the final use of production activities. Final use includes final consumption expenditure, total capital formation and net export of goods and services.
The quarterly GDP released by the National Bureau of Statistics is the result of accounting based on the production method.
1.2 Accounting Scope
1.2.1 Production scope
The production scope of GDP accounting includes the following four parts: first, the production of goods or services provided or prepared by producers to other units; Second, the self-sufficient production of all goods formed by producers for their final consumption or fixed capital; Third, the self-sufficient production of knowledge carrier products by producers for their final consumption or the formation of fixed capital, but it does not include similar activities undertaken by household departments; Fourth, the housing services provided by self-owned houses and the self-sufficient production of family and personal services provided by paid family service personnel. The production scope does not include unpaid family and personal services, natural activities without unit control (such as the natural growth of wild, uncultivated forests, wild fruits or berries, and the natural growth of fish in the high seas).
1.2.2 Main scope of production activities
The main scope of GDP production activities includes all permanent units with economic interest centers within the economic territory of China. The quarterly GDP data in this report is the national data accounted by the National Bureau of Statistics, excluding the regional GDP data of Hongkong, Macao Special Administrative Region and Taiwan Province.
1.3 Accounting Unit
GDP accounting mainly takes corporate units as accounting units. In accounting, corporate units are divided into different industries according to their main activities, and the added value of each industry is calculated separately, and then the added value of each industry is summarized to get GDP.
1.4 Accounting frequency
The accounting frequency is quarterly. From the first quarter of 1992 to the second quarter of 2015, China used the cumulative accounting method to calculate quarterly GDP, that is, the GDP data of the first quarter, the first quarter, the first quarter, the third quarter and the first quarter were calculated respectively, and the initial accounting of GDP in the first quarter and the fourth quarter was the initial accounting of annual GDP. From the third quarter of 2015, the quarterly accounting method was changed, that is, the GDP data of the first quarter, the second quarter, the third quarter and the fourth quarter of each year were calculated respectively, and the accumulated data was obtained by adding the data of the current quarter.
Since the first quarter of 2011, the National Bureau of Statistics has officially released the growth rate of GDP in each quarter.
1.5 Legal basis and system provisions
GDP accounting strictly abides by the provisions of the Statistics Law of the People’s Republic of China. At present, China’s GDP is calculated according to the requirements of China National Economic Accounting System (2016), which adopts the basic accounting principles, contents and methods of the United Nations National Accounts System (2008).
1.6 confidentiality
According to Article 9 of Chapter I of the Statistics Law of the People’s Republic of China, statistical institutions and statisticians shall keep confidential the state secrets, business secrets and personal information they know in their statistical work.
National accountants keep the unpublished professional statistical data and administrative records strictly confidential when conducting GDP accounting, and also keep the current GDP data strictly confidential before the release of GDP accounting data.
1.7 User demand
Domestic users of quarterly GDP data are mainly government departments, research institutions, universities, industry associations, media and the public. In addition, the National Bureau of Statistics regularly provides quarterly GDP data of China to the United Nations, the International Monetary Fund, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, the Asian Development Bank and other international organizations.
2. Quarterly GDP accounting method
2.1 classification system
In the quarterly GDP accounting, the industry classification is based on the China national economy industry classification standard and the third industry classification standard, and two classification methods are adopted.
The first classification is the national economic industry classification, which adopts the National Economic Industry Classification (GB/T 4754-2017) promulgated by the National Standards Administration in 2017. Two-level classification is adopted in actual accounting.
The first-level classification is based on the categories in the national economic industry classification, and it is divided into 11 industries, including agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, fishery, industry, construction, wholesale and retail, transportation, warehousing and postal services, accommodation and catering, finance, real estate, information transmission, software and information technology services, leasing and business services, and other industries. Among them, the industry includes mining, manufacturing, electricity, heat, gas and water production and supply industries; Other industries include scientific research and technical services, water conservancy, environment and public facilities management, residential services, repairs and other services, education, health and social work, culture, sports and entertainment, public management, social security and social organizations.
On the basis of the first classification, the second classification refines some categories in the national economic industry classification into industry categories.
The second classification is the classification of tertiary industries, which is divided into primary industry, secondary industry and tertiary industry according to the Regulations on the Classification of Tertiary Industries revised by the National Bureau of Statistics in 2018. The primary industry refers to agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery (excluding agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery professional and auxiliary activities); The secondary industry refers to mining industry (excluding mining professional and auxiliary activities), manufacturing industry (excluding metal products, machinery and equipment repair industry), electricity, heat, gas and water production and supply industry, and construction industry; The tertiary industry, namely the service industry, refers to other industries except the primary industry and the secondary industry (excluding international organizations).
2.2 Sources of information
In the quarterly GDP accounting, all available and applicable economic statistical survey data are used for GDP accounting. The data sources mainly include two parts:
First, the national statistical survey data refers to all kinds of statistical data obtained by the statistical survey conducted by the national statistical system, such as the statistical survey data of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery, industry, construction, wholesale and retail, accommodation and catering, real estate, service industries above designated size, population and labor wages, price statistics, etc.
Second, the administrative records of the administrative departments, mainly including the relevant data of the Ministry of Finance, the People’s Bank of China, the State Administration of Taxation, the CSRC and other administrative departments, such as the local and foreign currency credit receipts and payments of financial institutions of the People’s Bank of China and the tax information of the State Administration of Taxation by industry.
2.3 accounting methods
2.3.1 Accounting method of current value-added
According to the data sources, the quarterly current price value-added accounting mainly adopts the value-added rate method, the related value quantity index deduction algorithm and the current price calculation by using constant prices.
2.3.1.1 correlation value quantity index speed calculation algorithm
The speed calculation algorithm of related value index is to calculate the growth rate of current price added value by using the current price growth rate of related value index, and then multiply the current price added value by the calculated growth rate of current price added value in the same period of last year. The calculation formula is as follows:
Current value added = current value added in the same period of last year × (1+current value added growth rate)
Among them, the growth rate of current price added value is determined according to the growth rate of current price of relevant value indicators and the quantitative relationship between the growth rate of current price added value in previous years and the growth rate of current price of relevant value indicators.
2.3.1.2’s method of calculating current price by constant price
Firstly, the added value of constant price in this period is obtained by extrapolating the volume index, and then the added value of current price is calculated according to the relevant price index. The calculation formula is:
Current price added value = constant price added value × price index
2.3.2 Accounting method of constant price added value
Constant price added value is to convert the added value calculated at current price into the value calculated at a fixed period (base period), so as to eliminate the influence of price change factors and make the values in different periods comparable. The added value of constant price is calculated by the fixed base period method. At present, the base period is changed every five years, and the base period of constant price added value from 2021 to 2025 is 2020.
Quarterly constant price added value accounting mainly adopts price index reduction method and related volume index extrapolation method.
2.3.2.1 price index reduction method
Use the relevant price index to directly reduce the current price added value and calculate the constant price added value. The calculation formula is:
Constant price added value of an industry = current price added value of the industry ÷ price index
Extrapolation method of 2.3.2.2 mass index
Calculate the growth rate of constant price added value by using the growth rate of related material indexes, and then calculate the current constant price added value by using the constant price added value of the same period last year and the calculated growth rate of constant price added value. The calculation formula is:
Constant price added value of an industry = constant price added value of the industry in the same period of last year × (1+growth rate of constant price added value of the industry)
Among them, the growth rate of constant price added value is determined according to the growth rate of related material indexes in this period and the quantitative relationship between the growth rate of constant price added value in previous years and the growth rate of related material indexes.
2.4 seasonal adjustment
The growth rate of GDP is the result of comparing the quarterly added value with the data of the previous quarter. When calculating, we must eliminate the influence of seasonal factors on the time series, and use NBS-SA, a seasonal adjustment software of the National Bureau of Statistics, to adjust the time series seasonally. NBS-SA is developed on the basis of seasonal adjustment software commonly used in the world at present, taking into account the unique seasonal factors in China. The software adds a new module to deal with the seasonal factors unique to China, effectively eliminating the seasonal factors unique to China, including mobile holiday factors such as Spring Festival, Dragon Boat Festival and Mid-Autumn Festival, factors that change the working days from the original 6-day system to 5-day system, and factors brought about by holiday changes and holidays.
3. Revision of quarterly GDP data
3.1 the necessity of revision
The preliminary accounting of quarterly GDP has a strong demand for timeliness, and it is generally published about 15 days after the quarter. At this time, all the basic data needed for GDP accounting cannot be obtained, so the preliminary accounting of quarterly GDP is calculated by using professional statistical progress data and related indicators. After that, with the increasing and perfecting of available basic data, the GDP data will be revised by using more complete basic data, such as professional statistical annual reports, industry financial data and financial final accounts data, so as to reflect the actual situation of economic development more accurately.
3.2 Revision procedure
According to the latest reform of GDP accounting and data release system of National Bureau of Statistics, quarterly GDP accounting in China is divided into two steps: preliminary accounting and final verification. Usually, after the annual GDP is finally verified, the quarterly data should be revised, which is called routine revision; After the national economic census is carried out, new basic data that have great influence on GDP data are found, or the annual GDP historical data are revised after the calculation method and classification standard have changed, the quarterly GDP historical data should also be revised accordingly, which is called comprehensive revision.
3.3 Revision method
3.3.1 Revision of quarterly data
At present, the method of revising quarterly GDP data in China is proportional convergence method, that is, the method of adjusting quarterly data by using the difference between the annual benchmark value and the summary of the four quarters in the year. The basic method of proportional convergence is as follows: firstly, the current price and constant price added value of various industries in the national economy are connected respectively, and GDP and the added value of the three industries are the sum of the added values of the connected industries. The connection method between constant price GDP and the added value of constant price three industries is the same as the current price.
3.3.2 Revision of ring comparison data
Because the object of seasonal adjustment is time series data, when any quarter data in time series changes, it will affect the result of seasonal adjustment; Adding the latest quarter’s data to the time series will also make the previous quarter’s month-on-month data change more or less, which is the result of the automatic correction of the model. According to the principle of seasonal adjustment, in general, the data will be greatly affected in the period close to the latest data; In the period far away from the latest data, the data is less affected. For the convenience of users, the revised ring-on-ring data of the previous quarter will be released through the website of the National Bureau of Statistics while releasing the ring-on-ring data of the current period.
4. Quarterly GDP data quality evaluation
4.1 Evaluation of basic data
Relevant departments will test the quality of professional statistical data and administrative record data used in GDP accounting to ensure that the data reasonably reflect the actual situation of economic development. When the GDP accounting department gets these basic data, it will check the completeness and accuracy of the data again to ensure that these data meet the concept and requirements of GDP accounting.
4.2 Evaluation of accounting methods
In the GDP accounting, the GDP accounting department will revise China’s quarterly GDP accounting method according to the developing economic reality of China and the constantly improving national economic accounting standards, so as to ensure the rationality of the accounting method.
4.3 Evaluation of accounting results
After the quarterly GDP accounting results are obtained, it is necessary to check the coordination of GDP data, GDP data and related professional and departmental statistical data and macro data to ensure the coordination and matching between GDP data and other major data. A system is being established to evaluate the basic statistical data of various professions and departments with national economic accounting as the core framework.
4.4 Comparability of data
The China National Economic Accounting System (2016) adopted the basic accounting principles, contents and methods of the United Nations National Accounts System (2008), so the GDP data is internationally comparable.
The historical data of quarterly GDP was revised after the national economic census was carried out or the calculation method and classification standard changed, so the quarterly GDP time series since the first quarter of 1992 was comparable.
5. Quarterly GDP data release
5.1 Release time
The preliminary accounting figures of quarterly GDP are generally released around 15th after the quarter, and the final verification figures of quarterly GDP are generally released in January of the following year. For the release of major statistical indicators, the National Bureau of Statistics will indicate the release date in the "Major Statistical Information Release Schedule" released at the beginning of the year, and GDP data will be released according to the prescribed schedule.
5.2 Release method
The preliminary calculation of quarterly GDP is published in the press conference on quarterly national economic operation, the website of the National Bureau of Statistics and the Monthly Report of China Economic Prosperity; The final verification of quarterly GDP is published in the national statistical database and China Economic Prosperity Monthly. For the time series of quarterly GDP data since the first quarter of 1992, it can be queried through the national statistical database.