The Lancet: The number of new cancer cases and deaths in China ranks first in the world. You must know 23 common cancer-causing factors and 7 anti-cancer habits!
With the aggravation of aging, the data of cancer patients around the world began to increase. As the world’s most populous country, China’s cancer data is not optimistic. No matter the number of new cases or deaths, China ranks first in the world.
According to the latest global cancer burden data in 2020 recently released by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) of the World Health Organization,China has become a veritable "cancer country".
In 2020, there were 4.57 million new cancer cases in China, including 2.48 million males and 2.09 million females. In 2020, there were 3 million cancer deaths in China, including 1.82 million males and 1.18 million females.
This is much higher than the previously published data. Let’s take a look at the specific data analysis of China:
Both climbed to the top: China ranked first in the world in new cases and deaths.
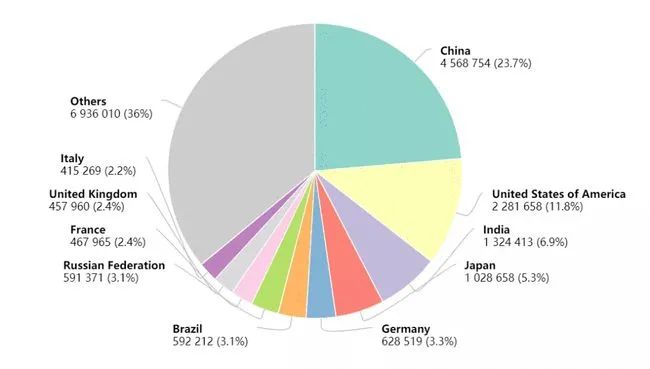
In 2020, there will be 19.29 million new cancer cases in the world, including 4.57 million new cancer cases in China, accounting for 23.7% of the world. As China is the world’s most populous country, the number of new cancer cases far exceeds that of other countries in the world.
The top ten countries with new cancer cases are: China 4.57 million, the United States 2.28 million, India 1.32 million, Japan 1.03 million, Germany 630,000, Brazil 590,000, Russia 590,000, France 470,000, Britain 460,000 and Italy 420,000.
Number of new cancer cases in various countries in 2020
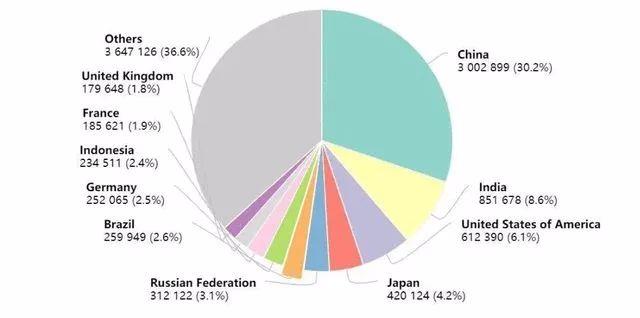
In 2020, there will be 9.96 million cancer deaths worldwide, including 3 million cancer deaths in China, accounting for 30% of the total cancer deaths, mainly due to the large number of cancer patients in China, which ranks first in the world.
The top ten countries with cancer deaths in 2020 are: China 3 million, India 850,000, the United States 610,000, Japan 420,000, Russia 310,000, Brazil 260,000, Germany 250,000, Indonesia 230,000, France 190,000 and Britain 180,000.
Number of cancer deaths in various countries in 2020
The supremacy of lung cancer is unshakable, and the death toll is far ahead.
In 2020, there will be 4.57 million new cases of cancer in China. Breast cancer ranks first in the world, but it ranks fourth after lung cancer, colorectal cancer and gastric cancer in China.
In 2020, the top ten cancers in China are: lung cancer 820,000, colorectal cancer 560,000, gastric cancer 480,000, breast cancer 420,000, liver cancer 410,000, esophageal cancer 320,000, thyroid cancer 220,000, pancreatic cancer 120,000, prostate cancer 120,000 and cervical cancer 110,000, which account for 78% of new cancers.
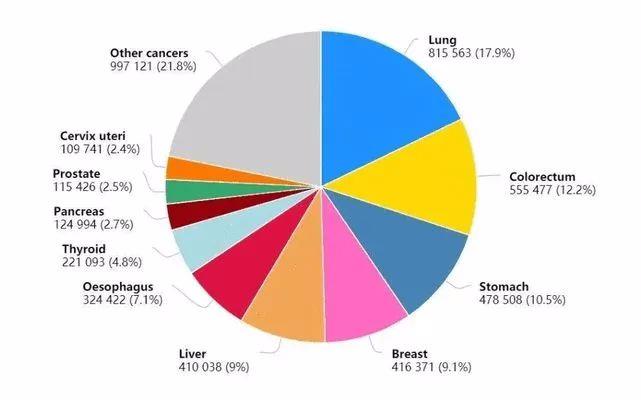
The Top Ten Cancer Types of New Cancer Cases in China in 2020
In 2020, the number of cancer deaths in China is 3 million, and the number of lung cancer deaths is far ahead, reaching 710,000, accounting for 23.8% of the total cancer deaths.
The top ten cancer deaths in China in 2020 are: lung cancer 710,000, liver cancer 390,000, gastric cancer 370,000, esophageal cancer 300,000, colorectal cancer 290,000, pancreatic cancer 120,000, breast cancer 120,000, nervous system cancer 70,000, leukemia 60,000 and cervical cancer 60,000, which account for 83% of the total cancer deaths.
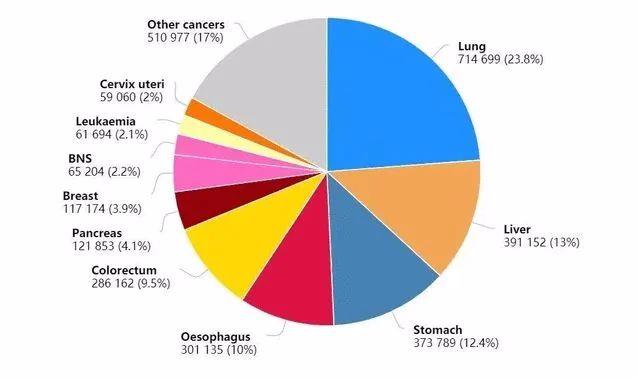
The top ten cancer types of cancer deaths in China in 2020
China male data: lung cancer, gastric cancer and liver cancer are still in the mountains.
In 2020, the number of new cancer cases among men in China is 2.48 million, accounting for 54% of the total, among which lung cancer, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer and liver cancer are the most common.
In 2020, the top ten cancers of male cancer cases in China are: lung cancer 540,000, gastric cancer 330,000, colorectal cancer 320,000, liver cancer 300,000, esophageal cancer 220,000, prostate cancer 120,000, pancreatic cancer 70,000, bladder cancer 70,000, thyroid cancer 50,000 and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma 50,000, which account for 84% of new male cancers.
Top Ten Cancer Types of Male Cancer Cases in China in 2020
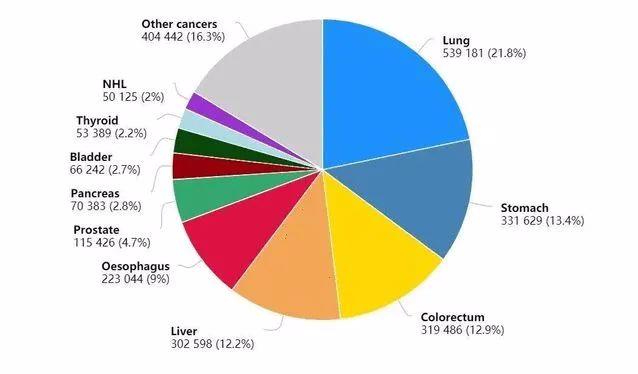
In 2020, the number of male cancer deaths in China was 1.82 million, accounting for 61% of the total, with lung cancer, liver cancer, gastric cancer and esophageal cancer accounting for the most deaths.
In 2020, the top ten cancers of male cancer deaths in China are: lung cancer 470,000, liver cancer 290,000, gastric cancer 260,000, esophageal cancer 210,000, colorectal cancer 160,000, pancreatic cancer 70,000, prostate cancer 50,000, leukemia 40,000, nervous system cancer 30,000 and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma 30,000, which account for 88% of the total cancer deaths.
The Top Ten Cancer Types of Male Cancer Death Cases in China in 2020
Women in China: New breast cancer surpassed lung cancer and topped the list.
In 2020, the number of new cancer cases among women in China is 2.09 million, accounting for 46% of the total, with breast cancer, lung cancer and colorectal cancer accounting for the largest number.
In 2020, the top ten cancers of new cases of female cancer in China are: breast cancer 420,000, lung cancer 280,000, colorectal cancer 240,000, thyroid cancer 170,000, gastric cancer 150,000, cervical cancer 110,000, liver cancer 110,000, esophageal cancer 100,000, endometrial cancer 80,000 and ovarian cancer 60,000, which account for 81% of new cases of female cancer.
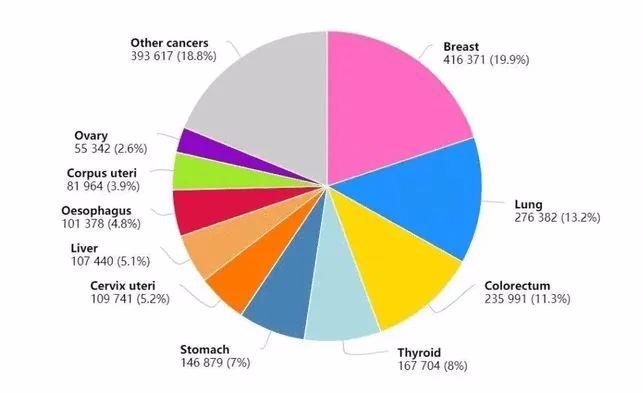
Top Ten Cancer Types of New Cases of Female Cancer in China in 2020
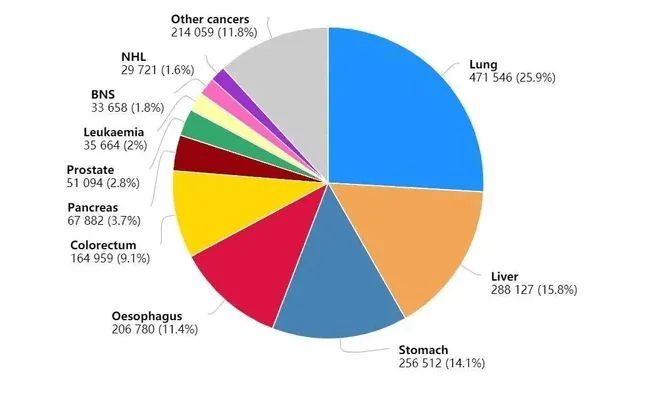
In 2020, the number of female cancer deaths in China is 1.18 million, accounting for 39% of the total, with lung cancer, colorectal cancer, gastric cancer and breast cancer accounting for the most deaths.
In 2020, the top ten cancers of female cancer deaths in China are: lung cancer 240,000, colorectal cancer 120,000, gastric cancer 120,000, breast cancer 120,000, liver cancer 100,000, esophageal cancer 90,000, cervical cancer 60,000, pancreatic cancer 50,000, ovarian cancer 40,000 and nervous system cancer 30,000, which account for 83% of the total cancer deaths.
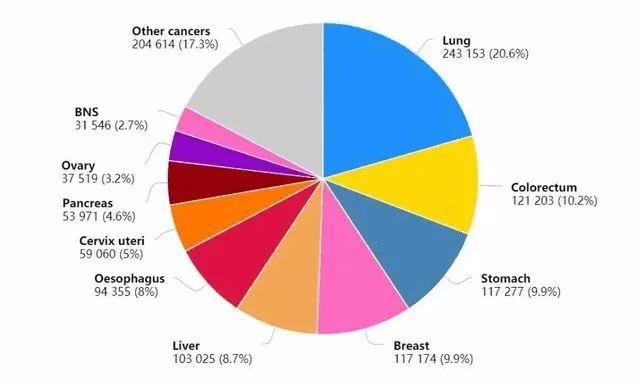
The top ten cancer types of female cancer deaths in China in 2020.
Globally, due to the aging of the population, it is estimated that the cancer burden will increase by 50% in 2040 compared with 2020, and the number of new cancer cases will reach nearly 30 million. This is most obvious in countries undergoing social and economic transformation.
For China, bringing cancer prevention and treatment intervention into the health plan will help to reduce the cancer burden in the future, and at the same time promote the development of innovative anti-cancer drugs. A two-pronged approach of "prevention and treatment" can better reduce the cancer burden and protect people’s health.
Recently, Academician He Jie and Professor Chen Wanqing from the National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital of China Academy of Medical Sciences led the publication of a heavy paper in The Lancet-Global Health.Aiming at China population, the incidence rate of 23 main cancer risks in China was analyzed.

The paper also further analyzes the proportion of cancer caused by various cancer risks in mainland provinces, municipalities and autonomous regions. When the public is facing these invisible killers around them, how should they actively respond and break them one by one?
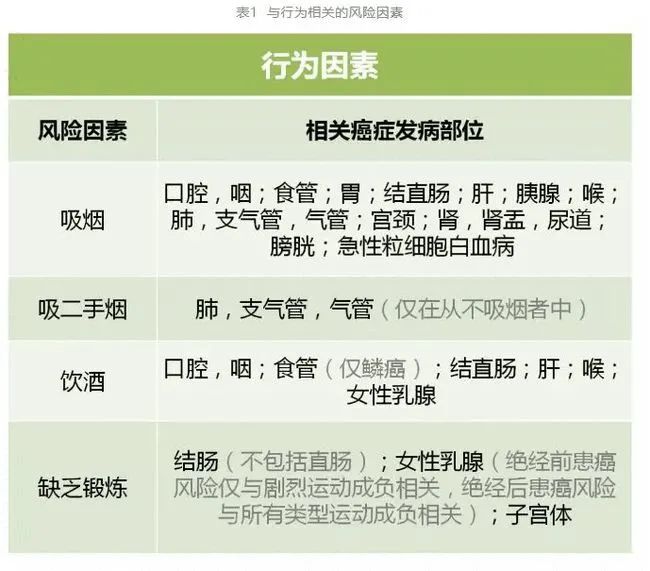
Common carcinogenic factors in China can be divided into five categories and 23 risk factors (see the table below for details):

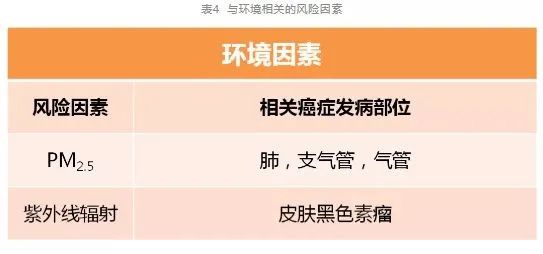
Proportion of cancer risk caused by various carcinogenic factors in provinces and cities
by23 avoidable causes of cancerProportion ranking, from high to low, the top five areHeilongjiang, Guangdong, Jilin, Hubei, Inner Mongolia; The five lowest proportions areGansu, Yunnan, Xinjiang, Tibet and ShanghaiAmong them, only 35.2% of cancer deaths in Shanghai are the lowest in the country.
Among the adults aged 20 and over, 1.036 million people in China die of various cancers caused by 23 major carcinogenic factors every year, accounting for 45.2% of all cancer deaths aged 20 and over (about 2.29 million people).
In other words, 45.2% of cancer deaths in China can be avoided as long as 23 carcinogenic factors are well controlled.
This means nearly 1.036 million preventable cancers. What should we do?
Do these seven points and break the 23 invisible killers!
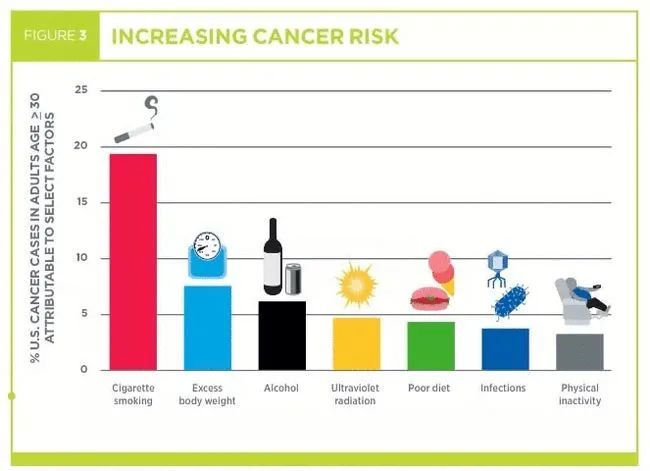
Quitting smoking is a top priority
The best cancer prevention strategy about smoking is never to smoke.
The biggest risk for women in six provinces, municipalities and autonomous regions in China is smoking, including Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Tianjin, Inner Mongolia and Anhui. For a long time, the incidence of lung cancer among women in Northeast China is relatively high, which is closely related to their high smoking rate.
In Guizhou and Yunnan, the proportion of male smokers accounts for 62.1% and 61.4%, and these two provinces also happen to be the provinces with the highest dependence on the tobacco industry.
For existing smokers, "the degree of risk reduction depends on the number of years you smoked and the number of cigarettes you smoked before quitting smoking." If you smoke for less than five years (no more than one pack a day), the risk of cancer is low. As long as you quit smoking, you will reduce your risk and get health benefits.
Smokers often retort: "I know that people who never smoke will still get lung cancer." Why should I quit smoking? " However, the scientific reality is that the less you smoke, the less chance you have of getting lung cancer.
If people adopt the living habits of low-risk groups, especially quitting smoking, about 80% to 90% of lung cancer deaths can be avoided. Since 1991, the cancer mortality rate in the United States has decreased by 26%, more than half of which is attributed to the decline in smoking rate.
Suggestions: 1. Quitting smoking is beneficial to people of any age. 2. Smoking shortens life expectancy by more than ten years. If you quit smoking before the age of 40, you can get back 9 years of life.
② Control drinking.
Alcohol is a class 1 carcinogen, and one out of every 18 cancers is related to drinking. There is ample evidence that alcohol will increase the risk of cancer in the oropharynx, larynx, esophagus (scale), stomach, liver, colorectal and breast, and some studies show that alcohol may also cause lung cancer, pancreatic cancer and skin cancer.
Tibet and Inner Mongolia are both famous for their boldness in drinking, and the proportion of cancer caused by drinking ranks first and second. Ningxia has the lowest proportion in the country, only 9%. Coincidentally, Hui people don’t drink.
The Dietary Guidelines for China Residents (2016 edition) suggests that men should not drink more than 25 grams of alcohol a day and women should not drink more than 15 grams, otherwise it is excessive drinking.
What is the concept of 25 grams of alcohol? Probably converted, please write down: white wine, no more than 1 Liang at a time; No more than one bottle of beer at a time; Red wine is limited to about one red wine glass at a time.
③ weight control
Obesity not only increases the risk of heart disease, diabetes, bone and joint diseases, but also increases the risk of cancer. Pancreatic cancer is especially mentioned here, which is not only related to obesity, but also related to diabetes.
The incidence of pancreatic cancer is higher in developed areas as a whole. Among women in Beijing, 6.7% are related to diabetes, which is the highest in the country. The proportions in Shanxi, Jiangxi and Guangxi are much lower. For example, only 1.5% of female pancreatic cancer in Jiangxi is related to diabetes.
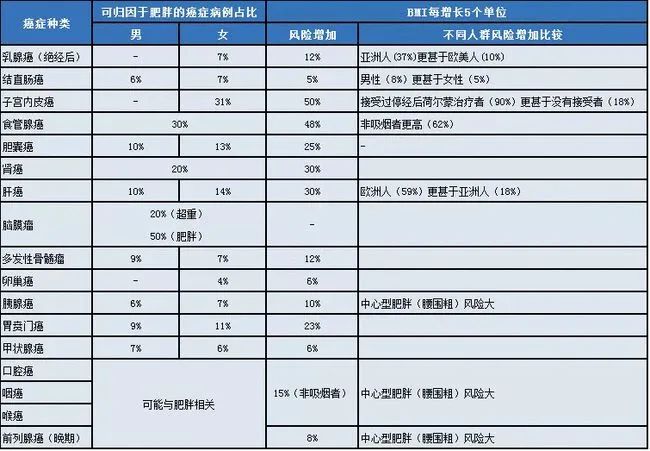
The relationship between various cancers and obesity is detailed in the table
Weight is kept within the standard BMI (body mass index), that is, 18.5 ~ 23.9.
Ps: body mass index (BMI)= weight (kg)÷ height 2 (m)
In addition, the waist circumference of men should be controlled within 90 cm; Women’s waistlines should not exceed 80 cm.
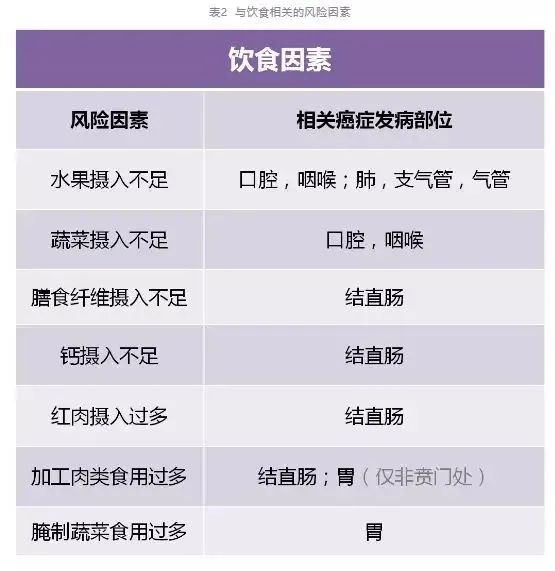
④ Healthy diet
Bacon, ham, sausage and hot dog are all listed as the first group carcinogens by the World Health Organization. Eating processed meat increases the risk of colorectal cancer by 18%.
Red meat can also shorten people’s life span and increase the risk of colon cancer, especially when the meat is roasted or barbecued, or even slightly burned. Although the cancer risk of red meat is far less than that of smoking, reducing the intake of red meat and limiting the consumption of processed meat will only reduce your risk of cancer.
As a whole, the first cancer risk factor in China is insufficient intake of fruits and vegetables, accounting for 15.6%, which is also the first risk factor for women in 14 provinces in China.
Dietary Guidelines for China Residents recommends eating 300-500g vegetables and 200-350g fresh fruits every day. Here, it should be emphasized that vegetables should be "non-starch vegetables", that is, vegetables that are not mainly starch, including all kinds of leafy vegetables, cruciferous vegetables (such as broccoli), okra, eggplant, etc., are non-starch vegetables, but do not include potato, sweet potato and yam.
Studies have shown that non-starch vegetables and fruits can reduce the risk of many upper respiratory and digestive tract tumors, such as oral cavity, nasopharynx, esophagus, lung, stomach and colorectal cancer.
⑤ Increase exercise.
Physical exercise not only helps to lose weight or keep fit, but also has a preventive effect on cancer. Exercise seems to reduce hormone levels, improve the function of our immune system, reduce the levels of insulin and insulin-like growth factors, and also reduce body fat.
Studies have shown that people who take at least 30-60 minutes of moderate to high-intensity physical exercise every day have a lower risk of cancer, especially breast cancer and colon cancer. In addition, the incidence of several other cancers has also decreased, including prostate cancer, lung cancer and endometrial cancer.
In order to prevent cancer, American sports guidelines suggest that adults should do at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise (such as brisk walking) every week; Or 75 minutes of high-intensity exercise (such as jogging); Or an equal amount of combination of two movements.
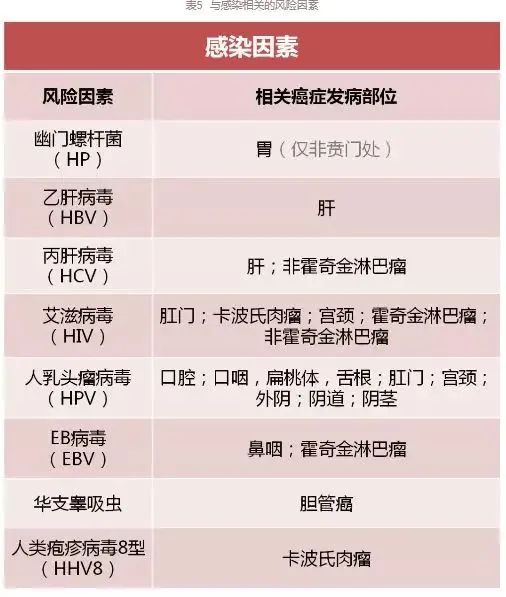
⑥ Stay away from pathogens.
For common infections in general life, the following table is recommended:
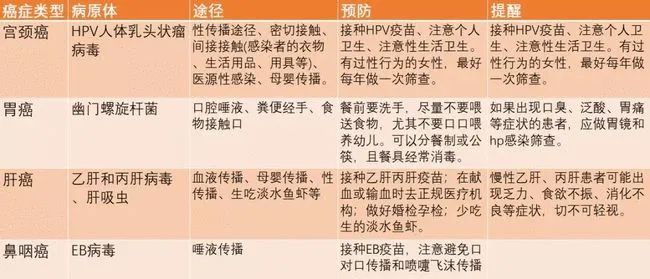
⑦ Screening for cancer.
For most cancers, if they can be found and treated early, the survival will be even greater. The following cancer screening should be conducted regularly:
Breast cancer screening, cervical cancer screening, colorectal cancer screening, hepatitis C virus screening, HIV screening, lung cancer screening, obesity and so on.
Source: Medical Elite Society